
Mannitol
Name: Mannitol
Molecular Structure:
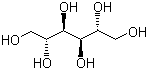 Molecular Formula: C6H14O6
Molecular Weight: 182.17
CAS Number: 87-78-5
EINECS: 201-770-2
Mannitol is an organic compound used as an osmotic diuretic agent and a weak renal vasodilator. Mannitol was originally isolated from the secretions of the flowering ash, called manna after their resemblance to the Biblical food, and is also be referred to as mannite and manna sugar. Mannitol is a sugar alcohol, that is, Mannitol is derived from a sugar by reduction. Other sugar alcohols include xylitol and sorbitol. Aqueous solutions of mannitol are mildly acidic and sometimes such solutions are treated to raise the pH.
Mannitol is used clinically to reduce acutely raised intracranial pressure until more definitive treatment can be applied, e.g. after head trauma. Mannitol is also used to treat patients with oliguric renal failure. Mannitol is administered intravenously, and is filtered by the glomeruli of the kidney, but is incapable of being resorbed from the renal tubule, resulting in decreased water and Na+ reabsorption via its osmotic effect. Consequently, mannitol increases water and Na+ excretion, thereby decreasing extracellular fluid volume.
Mannitol can also be used to open the blood-brain barrier by temporarily shrinking the tightly coupled endothelial cells that make up the barrier. This makes mannitol indispensable for delivering various drugs directly to the brain. Mannitol is commonly used in the circuit prime of a heart lung machine during cardiopulmonary bypass. The presence of mannitol preserves renal function during the times of low blood flow and pressure, while the patient is on bypass. The solution prevents the swelling of endothelial cells in the kidney, which may have otherwise reduced blood flow to this area and resulted in cell damage.
Mannitol is also being developed by Australian pharmaceutical company as a treatment for cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis and as a diagnostic test for airway hyperresponsiveness. The mannitol is orally inhaled as a dry powder through what is known as an osmohaler and osmotically draws water into the lungs to thin the thick, sticky mucus characteristic of cystic fibrosis. This is intended to make it easier for the sufferer to cough the mucus up during physiotherapy. The critical characteristic of the mannitol is its particle size distribution.
Mannitol is also the first drug of choice for the treatment of acute glaucoma in veterinary medicine. Mannitol is administered as a 20% solution IV. Mannitol dehydrates the vitreous humor and thus lowers than the intraocular pressure. However, it requires an intact blood-ocular barrier to work. Mannitol can also be used to temporarily encapsulate a sharp object (such as a helix on a lead for an artificial pacemaker) while Mannitol is passed through the venous system. Because the mannitol dissolves readily in blood, the sharp point will become exposed at its destination. Mannitol may be administered in cases of severe Ciguatera poisoning. Severe ciguatoxin, or "tropical fish poisoning" can produce stroke-like symptoms. Mannitol is the primary ingredient of Mannitol Salt Agar, a bacterial growth medium, and is used in others. In oral doses larger than 20 g, mannitol acts as an osmotic laxative, and is sometimes sold as a laxative for children.
Mannitol is also used as a sweetener for people with diabetes. Since mannitol has a positive heat of solution, it is used as a sweetener in "breath-freshening" candies, the cooling effect contributing to the fresh feel. The pleasant taste and mouthfeel of mannitol also makes it a popular excipient for chewable tablets. Mannitol is sometimes used as an adulterant or cutting agent for heroin, methamphetamines or other illicit drugs. In popular culture, when it is used in this manner, it is often referred to as baby laxative. |