
Lisinopril
Name: Lisinopril
Synonyms: N-{N-[(S)-1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]-L-lysyl}-L-proline
Molecular Structure:
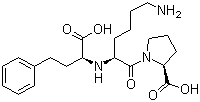 Molecular Formula: C21H31N3O5
Molecular Weight: 405.49
CAS Number: 76547-98-3
EINECS: 278-488-1
Lisinopril is a drug of the angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor class that is primarily used in treatment of hypertension, congestive heart failure, heart attacks and also in preventing renal and retinal complications of diabetes. Lisinopril has been compared with omapatrilat which is of similar function. Historically, lisinopril was the third ACE inhibitor, after captopril and enalapril, and was introduced into therapy in the early 1990s. Lisinopril has a number of properties that distinguish it from other ACE inhibitors: Lisinopril is hydrophilic, has long half-life and tissue penetration and is not metabolized by the liver.
Lisinopril is in a group of drugs called ACE inhibitors. ACE stands for angiotensin converting enzyme. Lisinopril is used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension), congestive heart failure, and to improve survival after a heart attack. Lisinopril may also be used for purposes other than those listed in this medication guide. |