
Itraconazole
Name: Itraconazole
Synonyms: 2-Butan-2-yl-4-[4-[4-[4-[[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl methyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]piperazin-1-yl]phenyl]-1,2,4-triazol-3-one; Oriconazole; Sporanox
Molecular Structure:
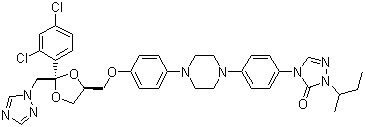 Molecular Formula: C35H38Cl2N8O4
Molecular Weight: 705.63
CAS Number: 84625-61-6
Itraconazole is a triazole antifungal agent that is prescribed to patients with fungal infections. Itraconazole may be given orally or intravenously. Itraconazole is antifungus with three azole rings. Itraconazole has antibiotic function both to deep and surface fungus. In clinical Practice, Itraconazole is mainly used in the treatment of systems infection Caused by deep fungi and candida. Itraconazole has a broader spectrum of activity than fluconazole (but not as broad as voriconazole or posaconazole). In particular, Itraconazole is active against aspergillus, which fluconazole is not. Itraconazole is also licenced for use in blastomycosis, histoplasmosis and onychomycosis. Itraconazole is over 99% protein bound and has virtually no penetration into cerebrospinal fluid. Therefore, Itraconazole should never be used to treat meningitis or other central nervous system infections. According to the Johns Hopkins Abx Guide, Itraconazole has "negligible CSF penetration, however treatment has been successful for cryptococcal and coccidioidal meningitis". Itraconazole is also prescribed for systemic infections such as aspergillosis candidiasis and cryptococcosi where other antifungal drugs are inappropriate or ineffective. |