
Ethambutol
Name: Ethambutol
Molecular Structure:
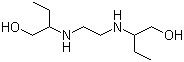 Molecular Formula: C10H24N2O2
Molecular Weight: 204.31
CAS Number: 74-55-5
EINECS: 200-810-6
Ethambutol (commonly abbreviated EMB or simply E) is a bacteriostatic antimycobacterial drug prescribed to treat tuberculosis. Ethambutol is usually given in combination with other tuberculosis drugs, such as isoniazid, rifampicin and pyrazinamide. Ethambutol is sold under the trade names Myambutol and Servambutol.
Ethambutol is bacteriostatic against actively growing TB bacilli, Ethambutol works by obstructing the formation of cell wall. Mycolic acids attach to the 5'-hydroxyl groups of D-arabinose residues of arabinogalactan and form mycolyl-arabinogalactan-peptidoglycan complex in the cell wall. Ethambutol disrupts arabinogalactan synthesis by inhibiting the enzyme arabinosyl transferase. Disruption of the arabinogalactan synthesis inhibits the formation of this complex and leads to increased permeability of the cell wall. Ethambutol is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and well distributed in body tissues and fluids, 50% is excreted unchanged in urine. |