
Chloramphenicol
Product Name:Chloramphenicol
Synonyms 2,2-Dichloro-N-[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(4-nitrophenyl)ethyl]acetamide; D-(-)-threo-2,2-Dichloro-N-[beta-hydroxy-alpha-(hydroxy-methyl)-p-nitrophenethyl]acetamide; Chloromycetin
Molecular Structure
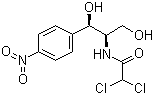 Molecular Formula:C11H12Cl2N2O5
Molecular Weight:323.13
CAS Registry Number:56-75-7
EINECS:200-287-4
Chloramphenicol is a bacteriostatic antimicrobial originally derived from the bacterium Streptomyces venezuelae, isolated by David Gottlieb, and introduced into clinical practice in 1949. It was the first antibiotic to be manufactured synthetically on a large scale, and alongside the tetracyclines, is considered the prototypical broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Chloramphenicol is effective against a wide variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, including most anaerobic organisms. Due to resistance and safety concerns, it is no longer a first-line agent for any indication in developed nations and has been replaced by newer drugs in this setting, although it is sometimes used topically for eye infections. In low-income countries, chloramphenicol is still widely used because it is exceedingly inexpensive and readily available.
The most serious adverse effect associated with chloramphenicol use is bone marrow toxicity, which may occur in two distinct forms: bone marrow suppression, which is a direct toxic effect of the drug and is usually reversible, and aplastic anemia, which is idiosyncratic (rare, unpredictable, and unrelated to dose) and generally fatal. |