
Dopamine Hydrochloride
Name: 3-Hydroxytyramine hydrochloride
Synonyms: 4-(2-Aminoethyl)-1,2-benzenediol hydrochloride; 2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)ethylamine hydrochloride; 3,4-Dihydroxyphenethylamine hydrochloride; Dopamine hydrochloride
Molecular Structure:
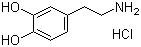 Molecular Formula: C8H11NO2.HCl
Molecular Weight: 189.64
CAS Number: 62-31-7
EINECS: 200-527-8
Dopamine hydrochloride is a catecholamine that works at a number of different receptor sites in the body depending on the dose at which it is administered. At lower doses Dopamine hydrochloride binds to dopamine receptors in the kidney, gut, brain and heart causing the blood vessels in these organs to widen. This improves the blood flow and therefore improves the amount of oxygen supplied to the organs. Dopamine hydrochloride also causes an increase in urine output from the kidneys. When the dose of dopamine is increased, beta-receptors, which are found on the heart muscle, are also activated. This causes an increase in the rate and strength at which the heart beats. Dopamine hydrochloride allows blood to be pumped effectively around the body in conditions where the pumping ability of the heart is reduced. Shock is a state in which blood flow to and its passage through a tissue or organ is inadequate to sustain life. Dopamine hydrochloride is usually associated with very low blood pressure and the production of abnormally low volumes of urine, and may be caused by a variety of conditions. As dopamine improves blood flow to organs and increases the production of urine, Dopamine hydrochloride is useful in the treatment of shock. Dopamine hydrochloride is injected slowly into the veins (intravenous infusion) to treat shock, which may be caused by trauma, heart attack, open heart surgery, heart failure, kidney failure and severe bacterial infections of the blood. Dopamine hydrochloride can reduce blood flow to vital internal organs (shock) |