
Astaxanthin
Name:Astaxanthin
Synonyms :3,3'-Dihydroxy-beta,beta-carotene-4,4'-dione
Molecular Structure:
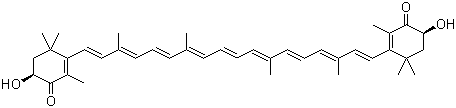 Molecular Formula :C40H52O4
Molecular Weight :596.85
CAS Registry Number :472-61-7
EINECS :207-451-4
Astaxanthin (pronounced as-tuh-zan'-thin) is a carotenoid. It belongs to a larger class of phytochemicals known as terpenes. It is classified as a xanthophyll, which means "yellow leaves". Like many carotenoids, it is a colorful, fat/oil-soluble pigment. Astaxanthin can be found in microalgae, yeast, salmon, trout, krill, shrimp, crayfish, crustaceans, and the feathers of some birds. Professor Basil Weedon was the first to map the structures of astaxanthin.
Astaxanthin, unlike some carotenoids, does not convert to Vitamin A (retinol) in the human body. Too much Vitamin A is toxic for a human, but astaxanthin is not. However, it is a powerful antioxidant; it is 10 times more capable than other carotenoids.
While astaxanthin is a natural nutritional component, it can be found as a food supplement. The supplement is intended for human, animal, and aquaculture consumption. The commercial production of astaxanthin comes from both natural and synthetic sources.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved astaxanthin as a food coloring (or color additive) for specific uses in animal and fish foods. The European Union (actually European Commission) considers it food dye within the E number system, E161j.
Astaxanthin is used as a feed supplement for salmon, crabs, shrimp, chickens and egg production. Regardless of the source, astaxanthin provides some important benefits beyond coloration. It also has been found to be essential for proper growth and survival.
Specification:
Packing:25kg/drum
Storage:be stored in shady,cool and dry place.keep away from toxic.
Shelf life:2years |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||