
Amygdalin / Vitamin B17
Name: Amygdalin
Synonyms: D-(-)-Amygdalin; (R)-Amygdalin; (R)-Amygdaloside; (R)-Laenitrile; (2R)-2-Phenyl-2-[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxan-2-yl]oxyacetonitrile
Molecular Structure:
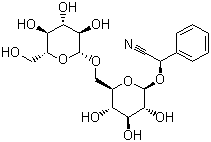 Molecular Formula: C20H27NO11
Molecular Weight: 457.43
CAS Number: 29883-15-6
EINECS: 249-925-3
Amygdalin is a kind of square crystal, melting point 200¡ãC, soluble in the water, ethanol, hardly soluble in the aether.
Amygdalin (also named as Vitamin B17) (from the Greek word for ¡®almond¡¯) is a substance found in the seeds of many kinds of fruits, such as plums, cherries, oranges, nectarines, apples and peaches, as well as in raw nuts, including bitter almonds. Apricots contain a particularly large amount of Vitamin B17 (amygdalin), and it¡¯s also abundant in plants such as clover, lima beans, millet, mung bean sprouts and sorghum. These are all highly nutritious foods with chemical contents that provide an excellent range of important benefits for the human body. As a result, many people have begun to call amygdalin ¡®vitamin B17¡¯.
Vitamin B17 was first discovered and isolated by two French chemists in the early 1800s, because they saw potential for the substance¡¯s role as a source of healing when combined with other nutrients. Since then, Vitamin B17 (amygdalin) compounds have been given several other scientific names, one of which is ¡®laetrile¡¯, an acronym of laevorotatory and mandelonitrile. You¡¯ll see this name used when it¡¯s describing a purified form of amygdalin AKA Vitamin B17. |