
Atenolol
Name: Atenolol
Synonyms: 4-(2'-Hydroxy-3'-((1-methylethyl)amino)propoxy)-benzeneacetamide;
Anselol; Apo-atenolol; Noten; Tenlol; Tenormin
Molecular Structure:
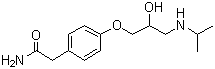 Molecular Formula: C14H22N2O3
Molecular Weight: 266.34
CAS Number: 29122-68-7
EINECS: 249-451-7
Atenolol (trade name Tenormin) can be used to treat cardiovascular diseases and conditions such as hypertension, coronary heart disease, arrhythmias, angina (chest pain) and to treat and reduce the risk of heart complications following myocardial infarction (heart attack). Atenolol is also used to treat the symptoms of Graves Disease, until antithyroid medication can take effect.
Due to its hydrophilic properties, the drug is less suitable in migraine prophylaxis compared to propranolol, because for this indication, atenolol would have to reach the brain in high concentrations, which is not the case.
Provisional data suggests that antihypertensive therapy with atenolol provides weaker protective action against cardiovascular complications (e.g. myocardial infarction and stroke) compared to other antihypertensive drugs. In particular, diuretics are superior. However, controlled studies are lacking.
Unlike most other commonly-used ¦Â-blockers, atenolol is excreted almost exclusively by the kidneys. This makes it attractive for use in individuals with end-stage liver disease. Dosage
In patients with normal renal function, the daily dose is 25 to 50 mg for the management of hypertension depending on the indication and severity of the disease. In most patients, the physician will start with a low initial dose and make increments in weekly intervals as tolerated. Dosage can vary from as little as 25 mg to 200mg a day. In cases of doses over 100mg, the dosage is usually divided and taken twice daily.
For the management of angina, 100mg daily may be given.
In patients with impaired renal function the daily dose should be reduced according to the clinical response of the individual patient. If a patient with end-stage renal failure is scheduled on regular dialysis, usually 50 mg are given after each dialysis procedure. In these patients, a severe hypotension may occur afterwards.
Specification: BP2005/USP28
Packing: 25kg/drum |